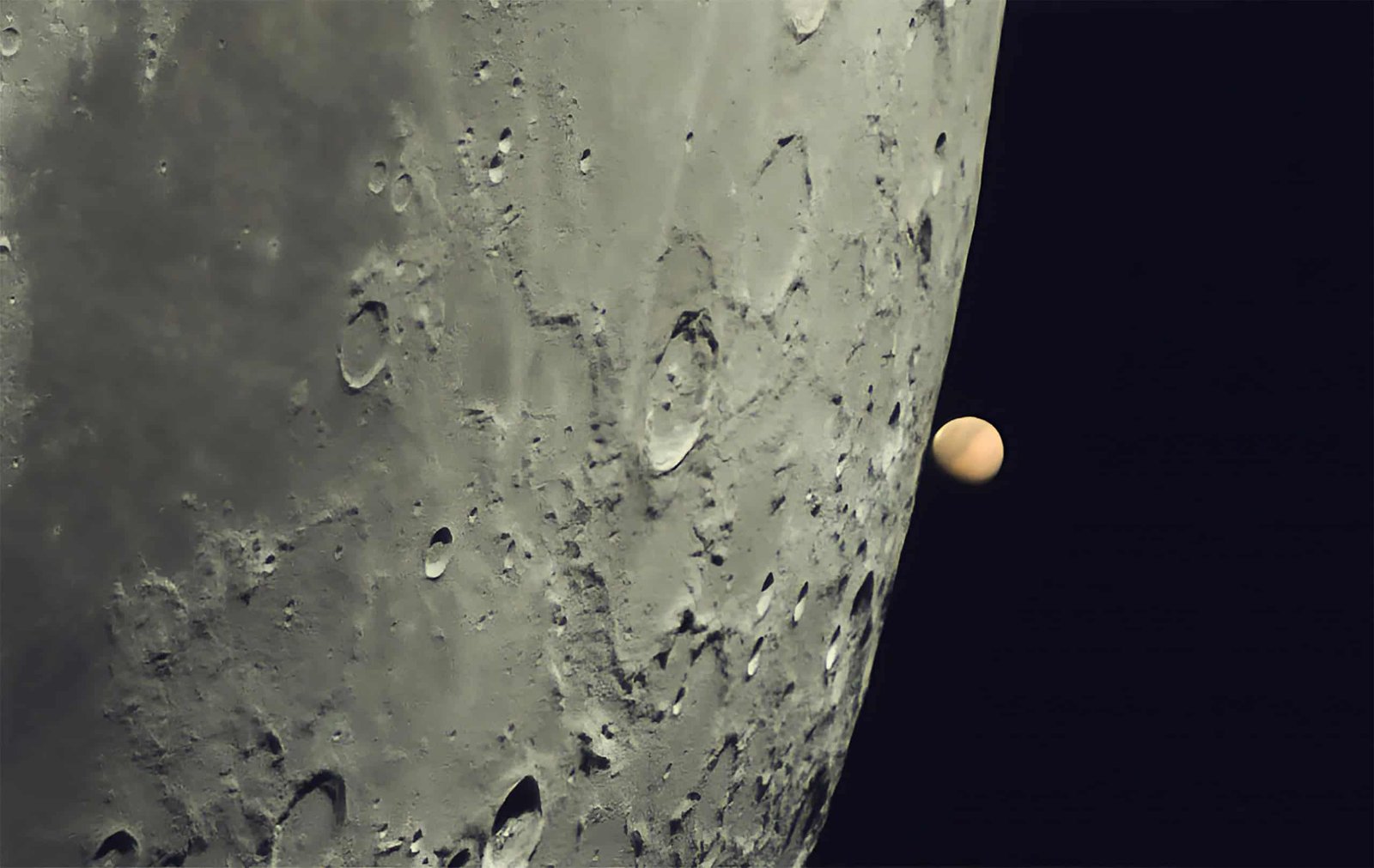
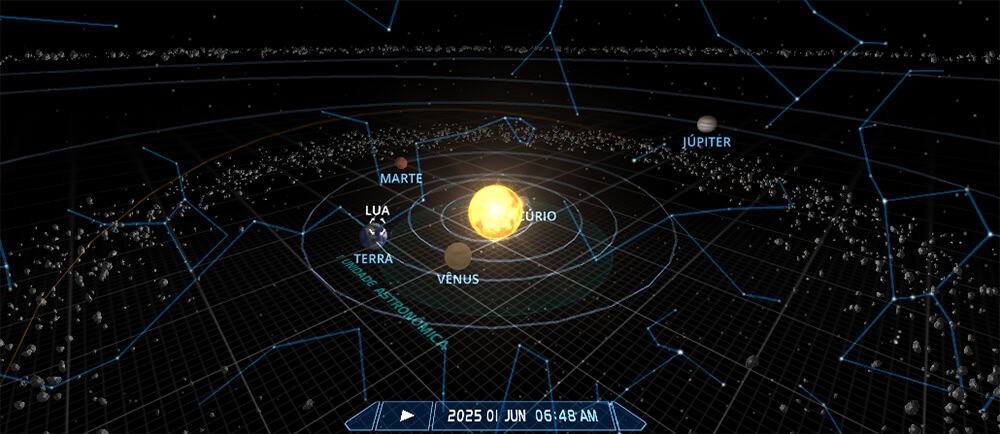
From the June tour of the planets of the solar system, the moon begins the month visiting Mars, in a phenomenon known as astronomical conjunction, when two or more stars share the same direct increase (coordinates equivalent to terrestrial latitude).
According to the observation guide Inhesky.orgThis happened at 6:48 AM (Hour of Brasilia) this Sunday (1). At that time, the Moon and Mars were below the horizon line, that is, they did not appear in the heavenly landscape. However, tonight, they can still be seen very close.
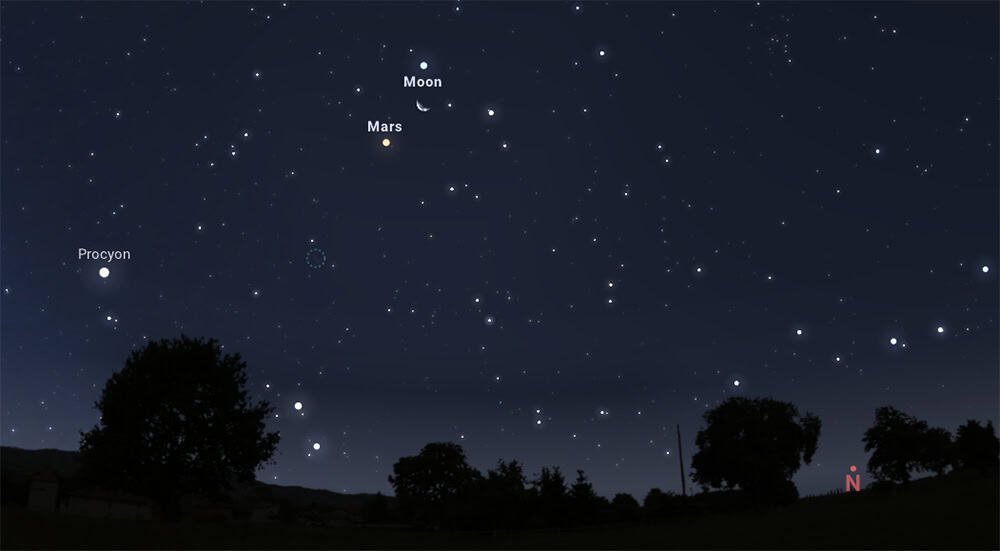
From Sao Paulo, for example, the couple will be visible in the north direction -west of the sky between 18h and 22h30, more or less. The moon will be in the magnitude of -11.4, while that of Mars will be 1.3, with both in the constellation of the Lion. The brighter an object is seen, the lower its magnitude (inverse relationship). The sun, for example, which is the brightest body in the sky, has an apparent magnitude of -27.
The couple will not be close enough to adapt to the field of view of a telescope, but will be visible in the naked eye or through a couple of binoculars.
But how do you know which little shining point near the moon will be Mars? Simple. By proximity to Earth, the planet always appears quite bright in the sky, and its characteristic red-red-makes color is very easy to identify it.
This time, it will be located south of the moon. So look at it, look for a brilliant orange ball underneath and see Mars ready.
After Mars, the moon passes through Saturn (19), Venus (22), Mercury (27), closing the month near the red planet (29). This series of conjunctions that the satellite makes monthly occurs because it orbits the Earth approximately on the same plane as the planets orbits the Sun, called the ecliptic plane.
Read -Ne More:
Why is Mars red?
The characteristic reddish tone of Mars has always attracted attention, evoking associations with gods and war operations. In Greek mythology, Ares, the god of war, was often linked to this color. Interestingly, the brightest star in the scorpion constellation, Antares, obtained this name for its reddish tone, which refers to the air, which means “anti-air”.
Later, with Roman rule in Europe, Ares was renamed Mars, a name that has also been given to the planet and remained in use to this day.
Marcian red tone is the result of a combination of complex factors. And this interaction occurs between the composition of the surface of the planet, its atmosphere and geological phenomena. Get more information here.




