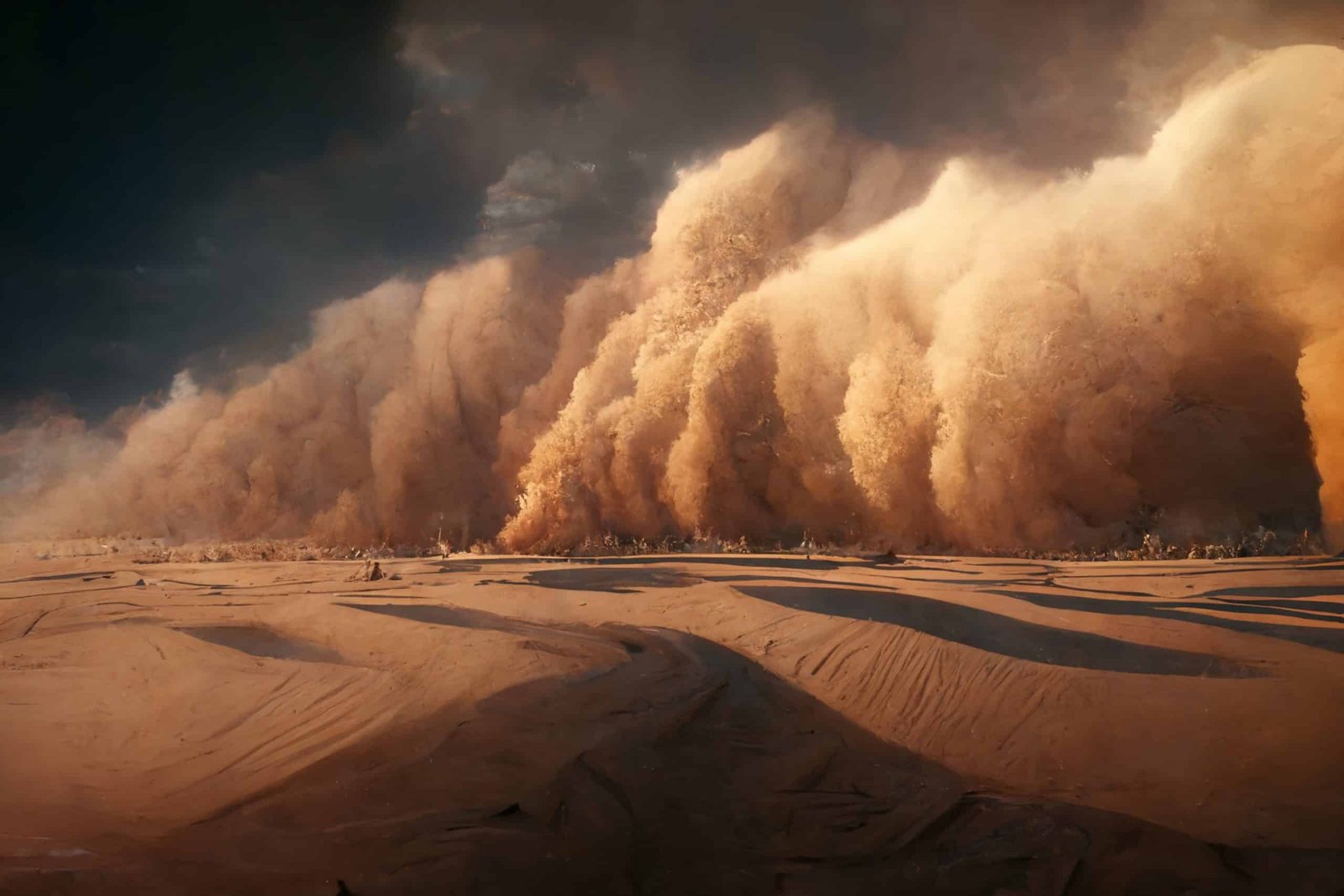
The inheritance of the Cold War these days go beyond the economic and social consequences, the nuclear tests performed in the period still make an unexpected mark. From time to time, the Sahara Desert is affected by a sandstorm that brings dust to Europe (and even other parts of the world), which happens that this pulse can lead to radiation.
A study by the Climate Laboratory and Environment of France and published in the journal Science Advances concluded that in 2022 a considerable amount of radioactive isotopes was present at the dust caused after a great storm that occurred in the Sahara.
In search of the origin of this radiation, scientists believed that isotopes came in nuclear tests performed at the time of the Cold War through France, between 1960 and 1966, when the country detonated 17 bombs in Sahara Algerian.
Read -Ne more
Even with the almost depopulated desert, thousands of local residents and French soldiers were exposed to radiation at that time. The most serious estimates suggest that up to 60,000 Algerians have been affected by the explosions.
But the places that this radiation can reach and its origin still surprises scientists.
The radioactive dust of the Sahara comes from an amazing origin
Despite the well -known evidence performed by France in the desert during the 1960’s, the radioactive dust that affected Europe involves radiation from the United States and the Soviet Union.
“This is because the power of detonation of French tests is only 0.02 percent of the total power of detonation of the USSR and the United States between 1950 and 1970. Many of the nuclear weapons tests of the USSR and North -Americans were performed at the same southern latitude and the accident of these tests can reach 8,000 meters and be dispersed by the wind,” said Yangjunjie Yangjie. Xu-Yang, lead author of the study of the Climate and Environment Sciences Laboratory in France, IFLSCENCE.
The researchers realized that the levels of plutonium did not correspond to the low isotopic reasons (below 0.07) of the nuclear tests of France. But in fact, they were estimated at 0.187, which is combined with the signatures of the United States and the Soviet Union.
But although it seems worrying, the amount of radiation present in this pulse is negligible, well below the limits established by the European Union and there is no risk to humans. “From my findings, the risk is insignificant,” Xu-Yang added.




