The relationship between geological failures and earthquakes is direct. Most earthquakes occur throughout the existing geological failures.
The rocks along a failure are under constant tension due to the movement of tectonic plates. This tension accumulates with the passage of time until the friction force between the rocks is overcome. At this point, the accumulated energy is released suddenly, causing an earthquake.
Geological failures are fractures or fracture areas in the Earth’s crust, where the rocks on both sides of the fracture moved to each other. This movement can be horizontal, vertical or a combination of both. Geological failures are the result of the tectonic forces acting on the earth’s crust for millions of years.
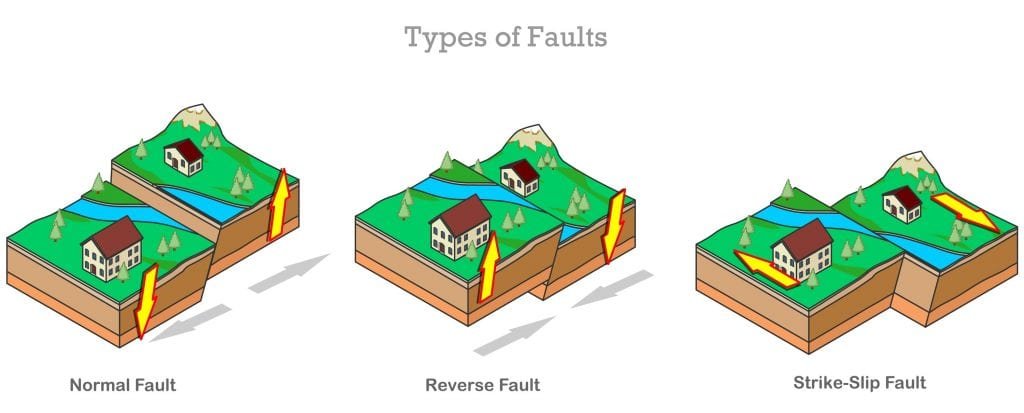
As shown in the previous illustration, there are three main types of geological failures, classified according to the type of movement that occurs throughout the fracture:
- Normal failureswhich occur when the earth’s crust extends, causing a block of rock to slide downward compared to the other.
- Reverse faultswhich occur when the earth’s crust is compressed, causing one block of rock to push to the other.
- Fallas that passwhich occur when the rocks move laterally by the failure in opposite directions.
What is the difference between geological failure and tectonic plate?
There is no way to talk about geological failures without interconnecting with tectonic plates. This is due to the fact that geological failures and tectonic plates are crucial elements of the Earth’s structure, closely interconnected and responsible for various geological phenomena that make up our planet. Although different, their concepts complement each other, and it is essential to understand their particularities in understanding the dynamics of the Earth.
The tectonic plates are large fragments of the lithosphere, the outer and rigid layer of the Earth, which encompasses the bark of the Earth and the part of the upper mantle. These plates, with a thickness ranging from 100 to 200 km, “fleet” on the mantle, a more viscous layer below the lithosphere and continuously moves at speeds ranging from a few millimeters to a year.
Eight main tectonic plates constitute most of the earth’s surface:
- American plate
- South -American Plate
- African dish
- Eurasian plate
- Plate
- Antarctic plate
- Pacific plate
- Nazca Plate
In addition to these, there are several smaller plates, such as the Philippines plate, the Arabic plate and the Caribbean plate.

That said, and the concept of geological failure already explained, we can understand that the relationship between geological failures and tectonic plates is fundamental. Geological failures are mainly a direct result of the interaction between the tectonic plates. The movement of the plates generates tensions in the earth’s crust that accumulates over time. When these tensions overcome the resistance to the rock, fractures occur, leading to geological failures.
Failures, therefore, are areas of weakness in the Earth’s crust that facilitate the movement between the tectonic plates. It is throughout these defects that most of the seismic activity focuses, giving rise to earthquakes of various magnitudes.
The tectonic plates are continuously moving, causing the rocks tension along the geological failures. When the accumulated tension exceeds the friction force between the rocks, energy is released suddenly, causing an earthquake.
The released energy spreads in the form of seismic waves that make the soil. The point of the earth’s surface directly above the breaking point of the failure is called epicenter. The rupture point in failure, where the earthquake originates, is called focus or hypocenter.
The study of geological failures is essential for understanding the emergence of earthquakes and evaluating seismic risk in different regions of the world. Through the mapping and analysis of geological failures, scientists can identify areas with a greater probability of earthquakes and estimate the maximum magnitude that can reach these events.
This information is crucial for urban planning, the construction of more secure structures and the implementation of measures of prevention and mitigation.
Read -Ne More:
The failure of San Andreas, located in California, the United States, is one of the most famous and studied geological failures in the world. It extends for about 1,300 km along the California coast and marks the boundary between the Pacific plate and the American plate.
The failure of San Andreas is classified as a failure of tracker or transformation. In this type of failure, the predominant movement is horizontal, with the plates that move laterally in opposite directions. In the case of San Andreas’s failure, the Pacific plate moves to the north -west, while the North -American plate moves to the south -East.
He is highly active and responsible for frequent earthquakes in California. The most famous was the 1906 Saint Francis earthquake, which destroyed much of the city and caused thousands of deaths.
Although not the most powerful earthquake ever recorded, the 1906 Saint Francis earthquake is a milestone in the history of the earthquake and has a warning of the importance of preparation and prevention in areas of seismic risk.

(Image: Jdjohansen / Shutterstock)
The failure of San Andreas is still a major concern for California, as scientists believe that it is able to generate great earthquakes in the future. The region is densely populated and houses important urban centers, such as Los Angeles and Sant Francesc, which increases the risk of lives and material damage in the event of a large earthquake.
Scientists who use various instruments are constantly controlled to measure seismic activity, failure movements and other relevant information. The aim is to better understand the behavior of failure and improve earthquake predictions, although forecasting needs are still a challenge for science.
The failure of San Andreas is an emblematic example of how geological failures can generate earthquakes and represent a risk to society. His study is essential for the advancement of seismology and for the implementation of measures to prevent and mitigate seismic risks worldwide.
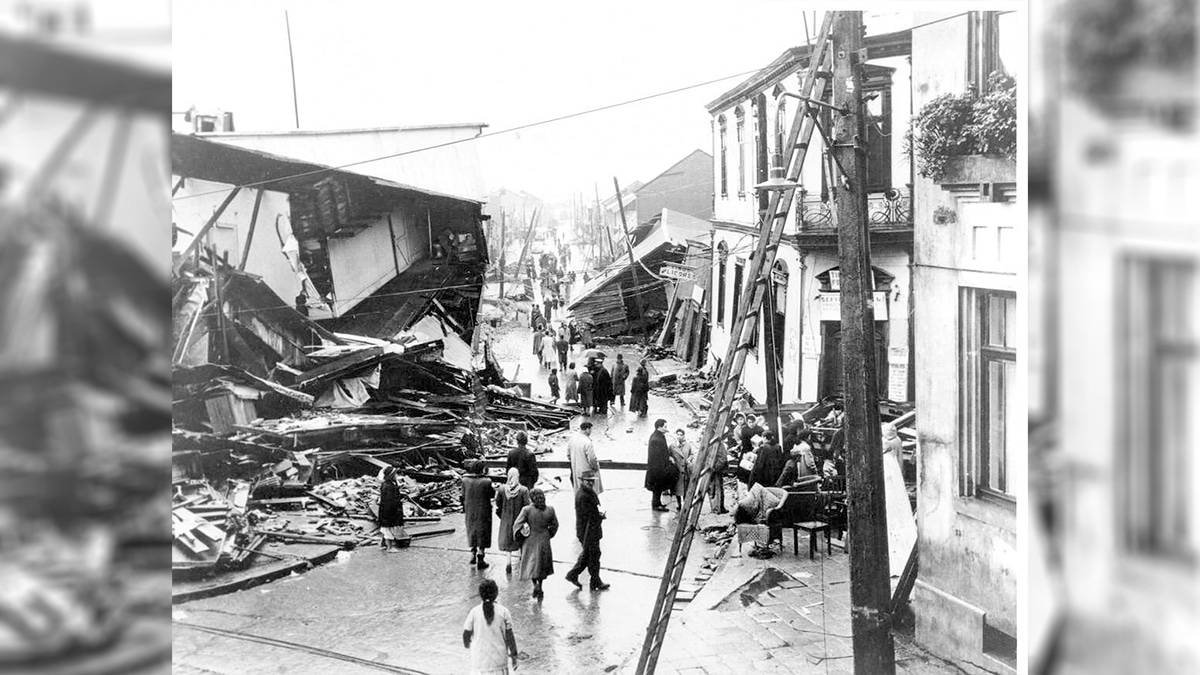
The most violent earthquake that is known, recorded by modern instruments, was the Great Chile earthquakeoccurred on May 22, 1960. It reached the magnitude of 9.5 On the Richter scale.
Location: Valdiva, Chile
Duration: About 10 minutes
Consequences:
– Devastation to much of southern Chile, with entire cities destroyed and severely damaged infrastructure.
– A giant tsunami that reached several areas of the Pacific Ocean, including Hawaii, Japan and the Philippines.
– Thousands of deaths and injured, although the exact number of victims has never been determined accurately.
– Significant environmental impact, including landslides, volcanic eruptions and changes in the course of the river.

For more information on the concepts of geological failure, the tectonic plate and the earthquake, you can search:
- United States Geological Survey), the United States Geological Service offers complete and updated information on tectonic plates, geological failures, earthquakes and other related phenomena. The site includes interactive maps, real -time seismic data, scientific articles and news about the latest events.
- CPRM (Brazilian Geological Service), the Brazilian geological service also provides information on tectonic plates and geological failures in Brazil, including risk maps and seismic activity studies in the country.




